Last updated on September 18th, 2025 at 04:49 pm
Words like accumulative and cumulative often trip people up because they seem interchangeable. But here’s the catch—they’re not.
While they share a root and both deal with growth or increase over time, they differ in nuance, tone, and usage across fields like education, finance, and even environmental science.
So what really sets these two apart? In short: accumulative focuses more on acquisition, while cumulative emphasizes sequence and progression.
Let’s dig into the details, clear up the confusion, and explore their real-world usage so you never second-guess them again.
“Accumulative” and “cumulative” both relate to growth, but they aren’t the same. Use accumulative when referring to the act of collecting or gathering (e.g., wealth or data), and cumulative when describing the build-up or result of a process over time (e.g., cumulative GPA or cumulative effects). Learn how to distinguish them clearly with real-world examples.
Understanding the Basics of Accumulative and Cumulative
At first glance, accumulative and cumulative both appear to describe something growing larger through additions. And yes—they do. But here’s the twist:
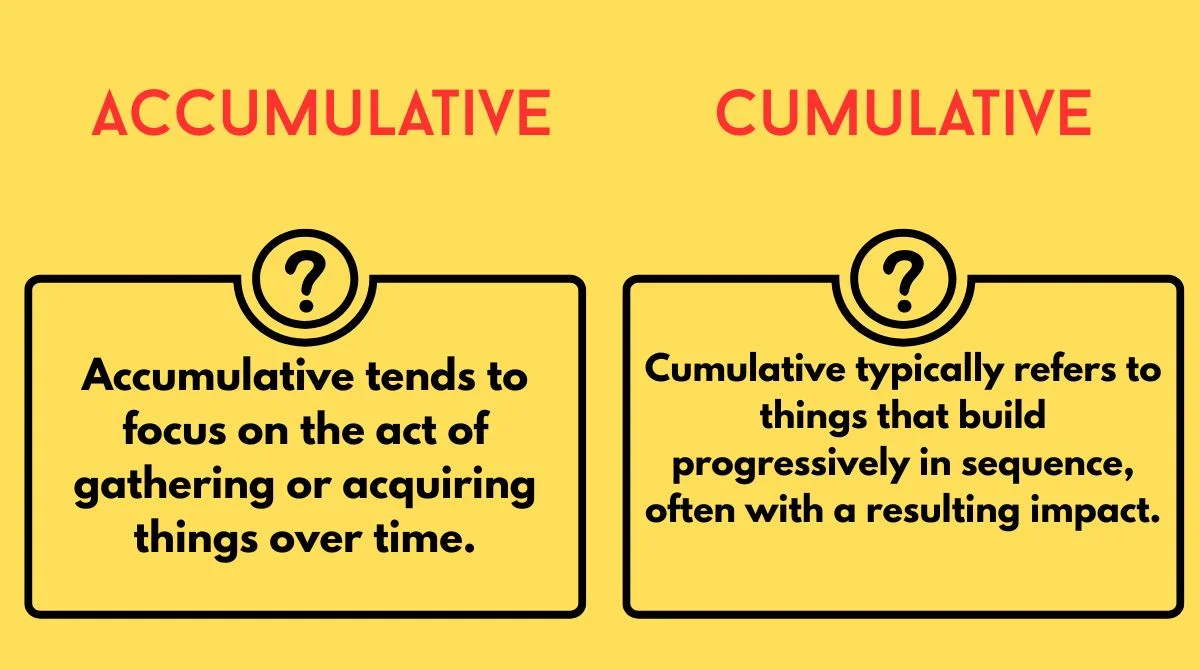
- Accumulative tends to focus on the act of gathering or acquiring things over time.
- Cumulative typically refers to things that build progressively in sequence, often with a resulting impact.
These words share a Latin origin—cumulare, meaning to heap up—but their modern usage has diverged in subtle yet significant ways.
Defining Accumulative: A Closer Look at Acquisitive Growth
Accumulative is an adjective used to describe a gradual gathering or acquisition of something, usually in a way that emphasizes the act of collecting or hoarding.
Characteristics of “Accumulative”:
- Implies intentional or organic collection.
- Often has a sense of ownership or control over what’s gathered.
- Common in psychology, behavior, and informal economics.
Examples:
- He developed an accumulative habit of saving coins from every country he visited.
- Her accumulative wealth grew steadily through smart investments.
Synonyms:
- Acquisitive
- Gathering
- Collecting
Breaking Down Cumulative: Successive Additions Over Time
Cumulative, on the other hand, speaks to a build-up over time—layered effects that often compound and result in an outcome or impact. It’s frequently used in scientific, educational, and technical contexts.
Characteristics of “Cumulative”:
- Implies ongoing sequence or progression.
- Focuses on the total result of successive steps or events.
- Often carries a quantifiable effect or consequence.
Examples:
- The cumulative effect of poor nutrition can lead to serious health problems.
- The student’s final grade was based on cumulative assessments.
Synonyms:
- Increasing
- Aggregated
- Compound
The Common Misconceptions and Misuses
Here’s where people get tripped up: they use these words interchangeably—but context is everything.
Common Errors:
- Saying “cumulative savings” when the emphasis is on intentional collection—better to use accumulative.
- Using “accumulative damage” in scientific contexts—cumulative is the correct term when referring to effects that build up over time.
Quick Fix Tip:
If you’re talking about the outcome of a process, use cumulative.
If you’re talking about the act of collecting, use accumulative.
The Nuances of Usage in Different Contexts
Let’s break down how each word shows up across different domains:
| Domain | Accumulative | Cumulative |
|---|---|---|
| Finance | Acquiring assets | Compounding returns |
| Education | Learning habits | Test formats |
| Science | Behavioral traits | Environmental impacts |
| Technology | User data collection | Software updates/effects |
| Psychology | Hoarding behavior | Stress buildup |
The takeaway? Accumulative often has a qualitative focus, while cumulative leans quantitative.
Exploring Examples in Real-World Scenarios
Understanding these words becomes easier when we apply them to relatable situations.
Example 1: Personal Growth
- Accumulative: Over the years, she developed accumulative knowledge from her travels.
- Cumulative: Her insights were the cumulative result of years of experience.
Example 2: Workplace Performance
- Accumulative: He gained accumulative respect through consistent leadership.
- Cumulative: His bonus reflected cumulative achievements over four quarters.
Example 3: Health & Lifestyle
- Accumulative: An accumulative diet of processed foods can change eating habits.
- Cumulative: The cumulative impact of lack of sleep is often underestimated.
Accumulative vs. Cumulative in Financial Terms
This is a domain where clarity matters most. Misusing these words could result in miscommunication or financial misunderstanding.
Accumulative in Finance:
Refers to gathering assets over time, often deliberately.
Examples:
- Accumulative savings account
- Accumulative investment strategy
Cumulative in Finance:
Refers to returns, interest, or impact over time.
Examples:
- Cumulative interest
- Cumulative return on investment
Tip: Use accumulative when referring to what’s being built up; use cumulative when referring to how it’s grown over time.
Educational Applications: Exam Types and Learning Processes
In education, the two terms are used very precisely, especially when describing testing styles and learning development.
Cumulative Testing:
Tests that cover all prior material up to the present.
- Encourages retention and integration of knowledge.
- Used in final exams, standardized testing.
Example:
The biology final was cumulative, testing everything from the first day of class onward.
Accumulative Learning:
Describes the gathering of skills and understanding over time.
- Implies a growing base of knowledge.
- Often informal or self-directed.
Example:
Her accumulative learning process helped her master coding outside of school.
Cumulative Effects and Sequences in Nature and Technology
In both environmental science and tech, cumulative effects are crucial to understanding large-scale patterns.
Cumulative Effects in Nature:
- Greenhouse gases contribute to cumulative climate change.
- Pollution has cumulative effects on marine life.
Cumulative Sequences in Tech:
- Software errors that build up over updates.
- Memory usage that causes cumulative slowdowns.
Meanwhile, accumulative might apply to how data is gathered or resources are compiled, but the lasting impact is cumulative.
Case Studies: Environmental and Data Progressions
Case Study 1: Environmental Impact
Scenario: An industrial plant emits low levels of toxins.
Accumulative: The company tracks accumulative emissions for compliance.
Cumulative: Over 10 years, the toxins create a cumulative health risk for nearby residents.
Case Study 2: Data Science
Scenario: A machine learning model processes user behavior.
Accumulative: The model collects accumulative data from multiple platforms.
Cumulative: The algorithm’s accuracy improves cumulatively as more data is analyzed.
Language Mastery: Tips for Remembering the Difference
Still not confident? Here are some quick memory tricks and tools:
Mnemonic Devices:
- Accumulative = Acquiring intentionally
- Cumulative = Compounding over time
Word Associations:
| Word | Think of… |
|---|---|
| Accumulative | Hoarding coins, growing a collection |
| Cumulative | Building blocks, a snowball effect |
Quick Quiz:
Choose the correct word:
The ___ GPA reflects your entire academic performance.
✅ Cumulative
She has an ___ habit of collecting antique watches.
✅ Accumulative

Faqs
What is the difference between accumulative and cumulative?
Accumulative refers to gathering or acquiring things over time, while cumulative refers to the increasing result or total impact of additions made over a period.
Can “accumulative” and “cumulative” be used interchangeably?
No, they are not truly interchangeable. While both involve growth, “accumulative” focuses on collection, and “cumulative” emphasizes resulting impact or total effect.
What does accumulative mean in finance?
In finance, “accumulative” refers to strategies focused on acquiring assets or savings over time, such as an accumulative savings plan.
What does cumulative mean in education?
“Cumulative” in education refers to assessments or grades that reflect the total performance across an entire course or curriculum.
Is it correct to say “cumulative savings”?
It depends on the context. If the emphasis is on gathered savings, “accumulative savings” is more precise. If highlighting total savings impact over time, “cumulative savings” may fit.
How can I remember the difference between accumulative and cumulative?
Think “accumulative = acquiring” and “cumulative = compounding.” Accumulative relates to what’s being gathered; cumulative relates to the final effect.
Final Thoughts: Why Word Precision Matters
Whether you’re writing a thesis, managing investments, or explaining climate change, the difference between accumulative and cumulative matters. One highlights the gathering, the other emphasizes the impact.
Use them precisely to sound more professional, avoid misunderstandings, and sharpen your writing.
If you’ve ever confused these two before, you’re not alone—but now, you’ve got the tools to keep them straight for good.
